



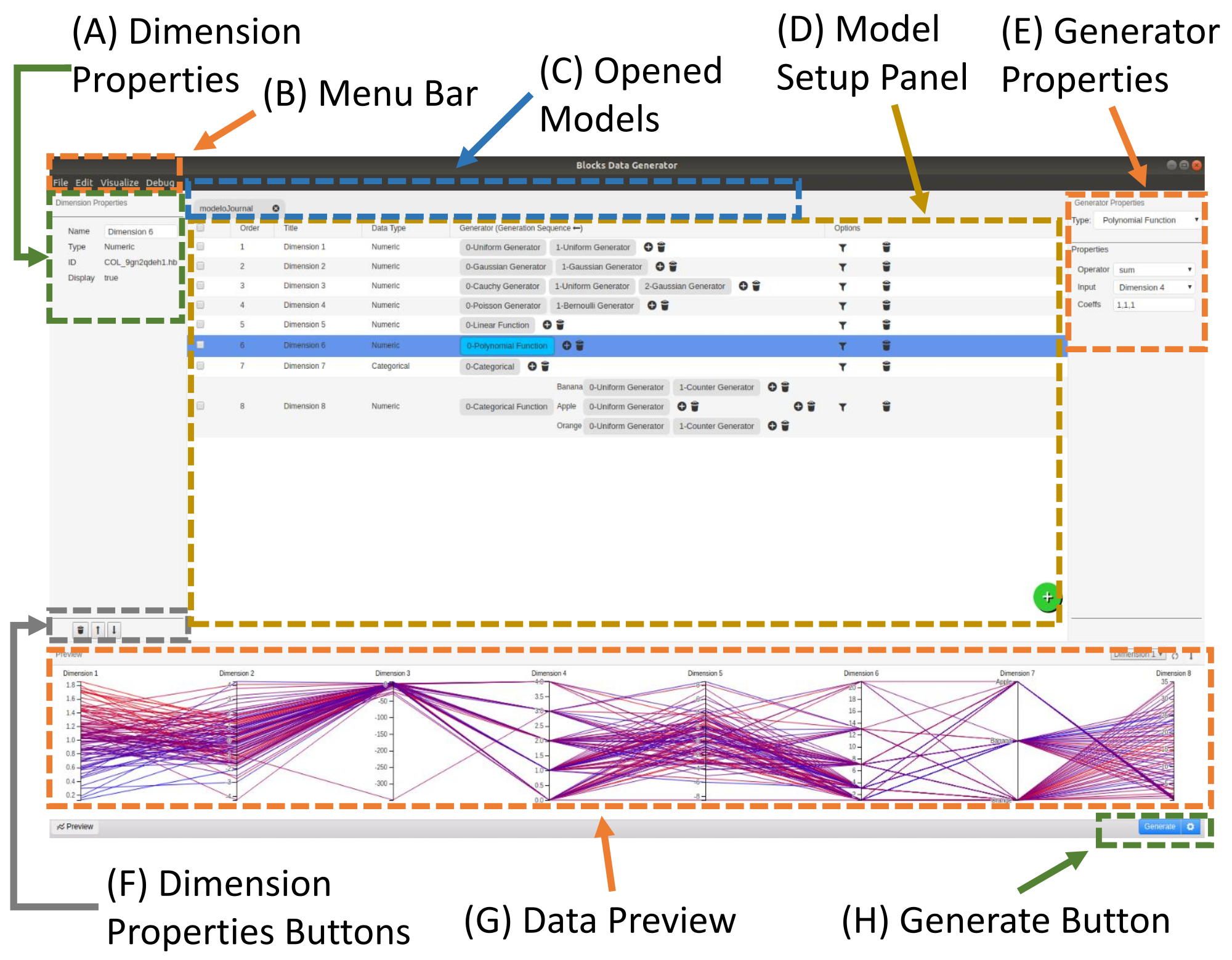
The evaluation is an essential step of works that propose new information visualization techniques or tools. A common type is the controlled experiment in which the researchers measure the user performance to execute specific tasks using the proposed method. Furthermore, the dataset used for these tests must contain known desired features to be evaluated (e.g., level of noise, the percentage of missing values) in a controlled way. Thus, this article proposes an application to generate synthetic databases for evaluating information visualization techniques and tools. The system aims to create a dataset generator model that allows the construction of datasets with a diversity of profiles in a controlled manner. The creator of the model can save it for future experiments or updates and can export it enabling other groups to replicate the experiments easily. For a better understanding of application features and how to use it, this work also shows two use scenarios explaining the created model for each situation.
One of the main challenges to creating rich, seamless, and adaptive Augmented Reality (AR) browsers is the accurate registration of the virtual contents in the real world. Usually, the AR browsers offer augmented navigation functionality by GPS and sensors, such as magnetometer and accelerometer. However, the position of virtual markers suffers some errors when the user is near to the desired location, due to many factors such as sensors failures and bad internet connections, among others. Additionally, to identify the correct marker, when there are many, is a challenging task to users. Therefore, to mitigate these problems, this paper proposes a hybrid approach of location and vision based tracking for AR applications, since the image recognition can be very helpful to identify near locations, avoiding misplaced markers and at the same time giving emphasis to that marker. Furthermore, to avoid bottlenecks in the AR browser applications the combination of the quality of vision-based tracking and the speed of the sensors is proposed. The designed system gets the information about the Points Of Interests (POIs), recommend places to explore around the user via GPS and sensors (as already done by current AR browsers) and run the recognition process only for the nearest POI to improve its registration. Aiming to choose the best recognition algorithm for this scenario, precision and time tests are performed using three algorithms (ORB, BRISK, and AKAZE) to detect keypoints and compute theirs features, and two algorithms (RANSAC and LMEDS) to estimate camera pose. The test pointed that the combination of AKAZE and RANSAC has the best accuracy, but an impractical time to use in real time application. Hence, the usage of vision techniques in an interval of time (skipping some frames) and the usage of inertial sensors movements to update the skipped frames are proposed, in order to use this solution on a mobile platform. Finally, the system solution was implemented in a tourism mobile AR application and some results are presented.
One of the main challenges to creating rich, seamless, and adaptive Augmented Reality (AR) browsers is the accurate registration of the virtual contents in the real world. Usually, the AR browsers offer augmented navigation functionality by GPS and sensors, such as magnetometer and accelerometer. However, the position of virtual markers suffers some errors when the user is near to the desired location, due to many factors such as sensors failures and bad internet connections, among others. Additionally, to identify the correct marker, when there are many, is a challenging task to users. Therefore, to mitigate these problems, this paper proposes a hybrid approach of location and vision based tracking for AR applications, since the image recognition can be very helpful to identify near locations, avoiding misplaced markers and at the same time giving emphasis to that marker. Furthermore, to avoid bottlenecks in the AR browser applications the combination of the quality of vision-based tracking and the speed of the sensors is proposed. The designed system gets the information about the Points Of Interests (POIs), recommend places to explore around the user via GPS and sensors (as already done by current AR browsers) and run the recognition process only for the nearest POI to improve its registration. Aiming to choose the best recognition algorithm for this scenario, precision and time tests are performed using three algorithms (ORB, BRISK, and AKAZE) to detect keypoints and compute theirs features, and two algorithms (RANSAC and LMEDS) to estimate camera pose. The test pointed that the combination of AKAZE and RANSAC has the best accuracy, but an impractical time to use in real time application. Hence, the usage of vision techniques in an interval of time (skipping some frames) and the usage of inertial sensors movements to update the skipped frames are proposed, in order to use this solution on a mobile platform. Finally, the system solution was implemented in a tourism mobile AR application and some results are presented.